Life in time with the heart
The heart is a fascinating and vital muscle pump that is often underestimated. In this article, we will explore the amazing function of the heart and why its health is crucial for our well-being. Discover how the heart pumps blood through our body and the role it plays in oxygen supply, nutrient delivery, waste elimination, hormonal regulation, and temperature control.
Small Muscle - Strong Performance
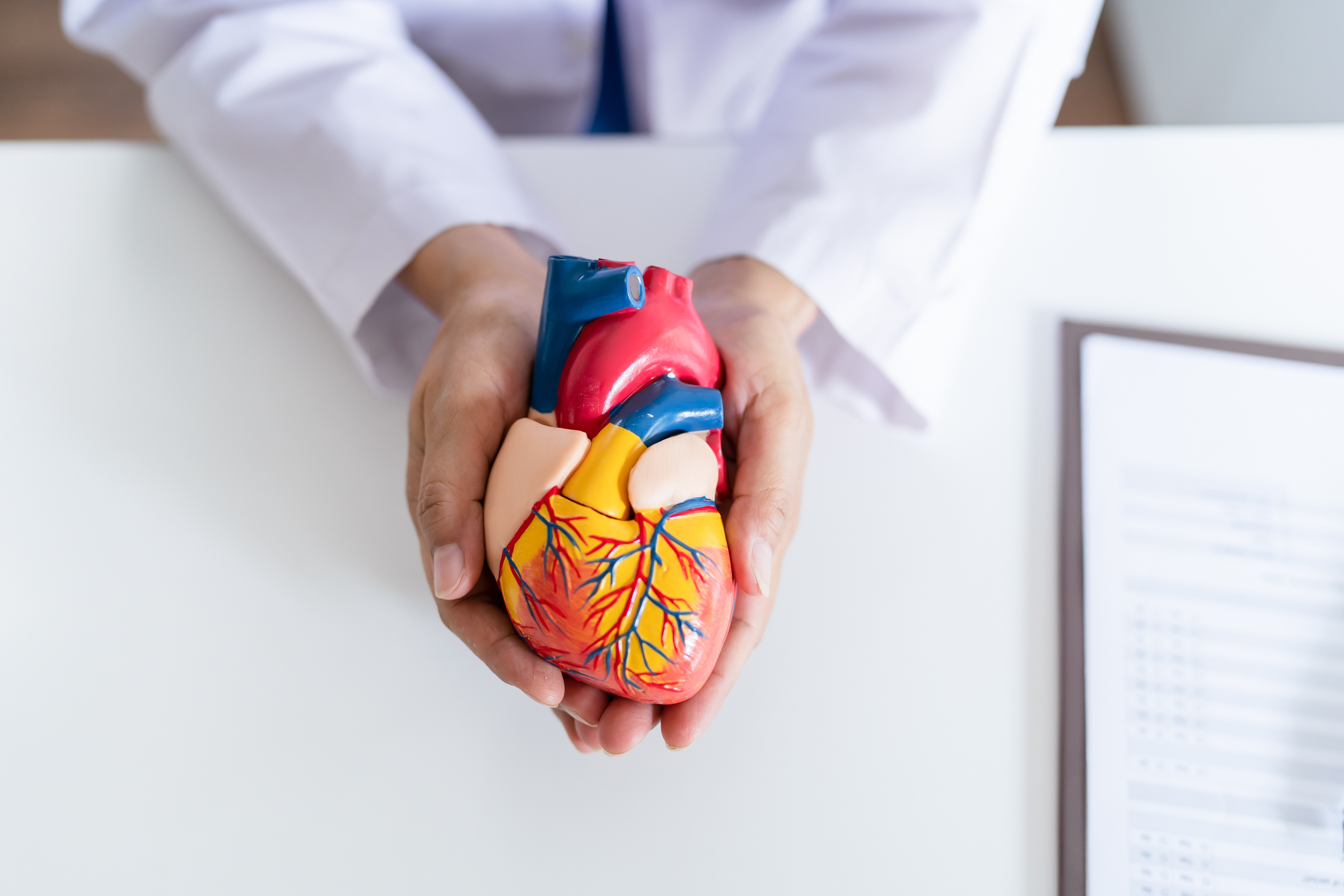
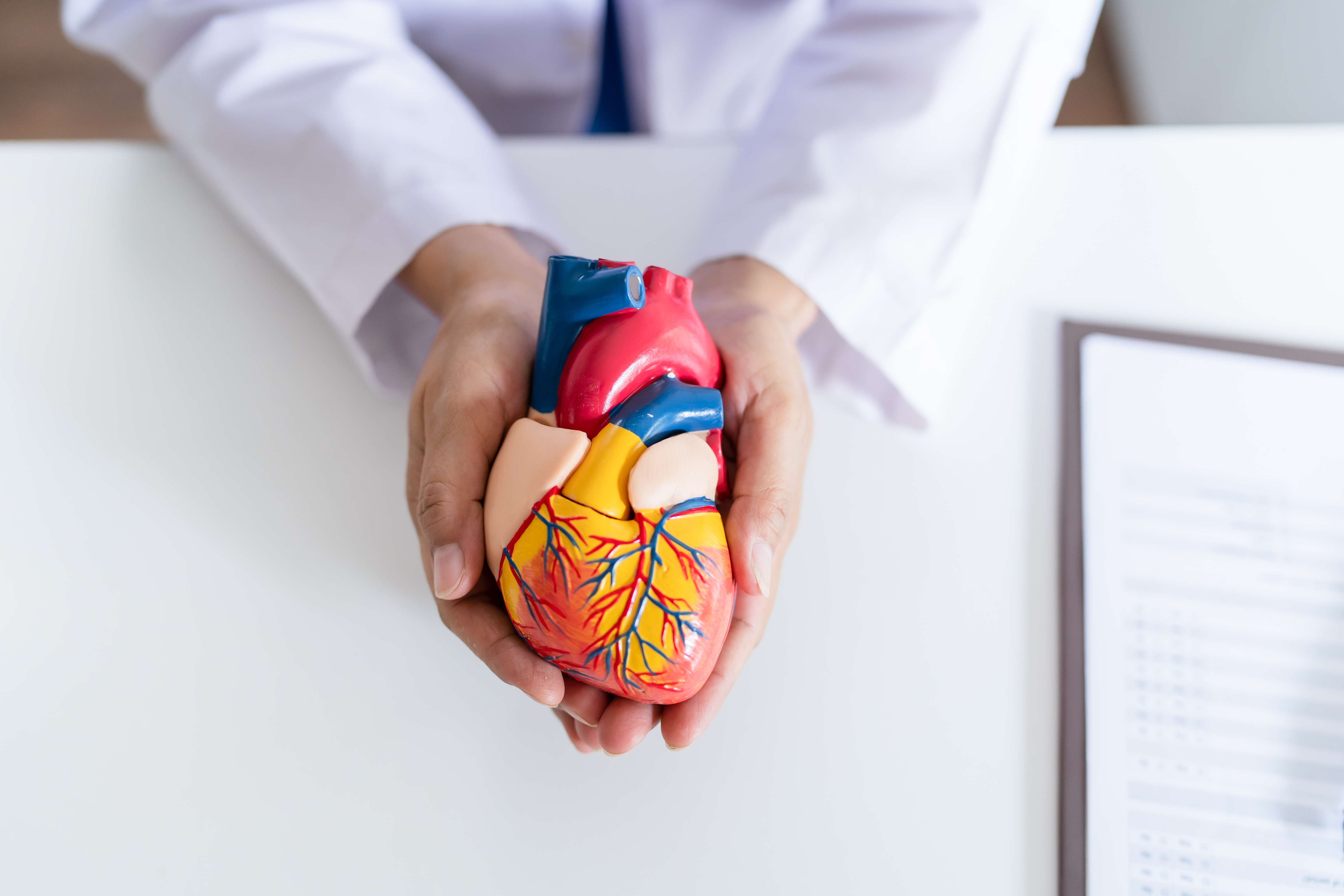
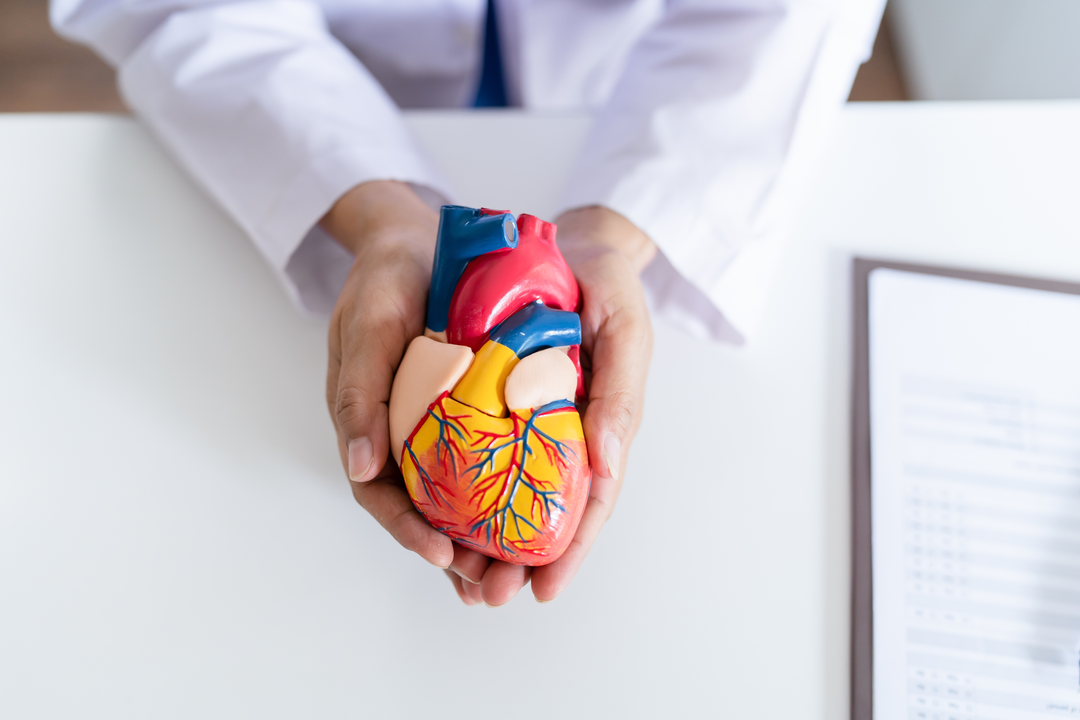
The heart, about the size of a closed fist, beats 60 to 100 times per minute, depending on age and physical condition, and even faster in extreme situations. Essentially, the heart is a powerful muscle pump that continuously propels blood through the entire vascular system of our body, which can be up to tens of thousands of kilometers long. This constant blood flow serves a multitude of vital functions for our body.
The Life Engine - Heart and Its Diverse Functions
Metaphors like "core," "You are my heart," and "One heart and one soul" are used where something is considered central or of the utmost importance. This symbolism is not accidental, as the heart, due to its many fundamental functions, plays a particularly crucial role in our viability and well-being:
🫁 Oxygen Supply: The heart is an tireless engine ensuring that our body is supplied with oxygen. Oxygen is absorbed through the lungs and released into our blood. The heart ensures that oxygen-rich blood is transported to every corner of our body. Oxygen is vital for our cells, needed to generate energy and keep us alive. Without the oxygen supply by the heart, our cells would not function, and our organism would weaken.
🍏 Nutrient Supply: The heart is also responsible for transporting nutrients such as glucose and amino acids to our cells. These nutrients are life's building blocks and play a crucial role in supporting the functions of our cells. Oxygen alone is not sufficient. The heart ensures that these vital substances efficiently reach the cells. The functionality of our cells is crucial for maintaining our health and supporting all vital bodily functions. Insufficiently supplied cells can have severe effects on our health, leading to various diseases.
🗑️ Waste Removal: Besides supplying oxygen and nutrients, the heart plays a crucial role in removing waste products. To generate energy, metabolic processes occur in our cells, consuming oxygen. This process produces carbon dioxide, which enters our blood through a diffusion process. The blood loaded with carbon dioxide is returned to the heart chambers through our venous system. Our heart captures the oxygen-poor, carbon dioxide-rich blood and pumps it into the pulmonary artery. In the lungs, a gas exchange occurs, where carbon dioxide is released from the blood into the small air sacs in the lung. From there, carbon dioxide is exhaled and removed from the body. Our kidneys also support this process by filtering our blood and excreting excess substances as urine. The elimination of waste products is necessary to prevent the accumulation of harmful metabolic waste products and ensure our well-being.
🧪 Hormonal Regulation: The heart not only influences blood flow but also plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and distributing hormones in our body. This is crucial to regulate various functions and processes in our organism. Disruption of hormonal balance can lead to diabetes, weight issues, thyroid disorders, infertility, and mental distress. Therefore, it is important to maintain hormonal production and regulation in the body in balance.
🌡️ Heat Transfer: The heart contributes to maintaining our body temperature. It responds to signals from the thermoregulation system to adjust the blood circulation of the skin and thus control heat dissipation. This mechanism helps keep our body temperature at an optimal level, ensuring normal physiological function. Our body temperature influences various physiological processes, including enzyme activity, the speed of chemical reactions, and the function of our organs.
Therefore, heart health is crucial to optimally supply our body with blood and nutrients, keeping it functional and healthy. If the heart does not function properly, the entire body may become non-functional in the worst case.
Cardiovascular Diseases - An Underestimated Public Enemy
The vital functions of the heart can be compromised by various cardiovascular diseases (CVD). According to the WHO, CVD comprises a group of heart and blood vessel diseases covering ICD-10 codes I05 to I79.
They can be grouped into:
- Coronary heart disease
- Cerebrovascular diseases
- Peripheral arterial diseases
- Rheumatic heart diseases
- Congenital heart diseases
- Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
CVD pose a significant problem today: they are the leading cause of death, accounting for around 45% in western countries and around 25% in developing countries of all deaths. Worldwide, approximately 17.3 million people die each year from the effects of cardiovascular diseases, with estimates projecting an increase to up to 23.6 million deaths by 2030.
CVD, alongside cancer, diabetes mellitus, and chronic respiratory diseases, are among the most important public health issues of the 21st century. It requires comprehensive measures (both preventive and in care) to be addressed. (Source: Austrian Ministry of Social Affairs, 2021).
Tracing the Causes of CVD
The causes of CVD are as diverse as the various types of diseases themselves: unfavorable lifestyle factors such as unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption